What kind of foot specialists are there? What is the difference between a paediatrician and a podiatrist? What exactly does a podiatrist and an orthopaedist do? How does a physiotherapist fit into everything and who to see for foot problems? Get to know the medical professions in foot health care.
Overview of experts
For simplicity, we list the representatives of the fields in the masculine gender, but you can also use the feminine gender at the same level (women often predominate in these fields). Specialist doctors often don't even use such specialised names and rather let themselves be represented by individual fields, or their expertise is intertwined across multiple fields. Therefore, when searching for specialist practices in the nearby area, it is best to use the profession itself, e.g. "physiotherapy", "podiatry", "orthopaedics", etc.
Paediatrician
Pediatrician - simply a pediatrician, more officially a general practitioner for children and adolescents. From birth, parents with children go to him for regular checkups and he takes care of the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of a variety of diseases typical for childhood. He has a medical degree and a versatile overview across specialties.
Therefore, the pediatrician should recognize irregularities in the healthy development of the child's feet and recommend a visit to an appropriate specialist depending on the nature of the problem. If you are unsure, see a paediatrician first. In adulthood, this function is then taken over by a general practitioner, also referred to as an adult general practitioner.
Podiatrist
A podiatrist is a specialist in feet, their anatomy, diagnosis of problems and treatment. In addition to joints, bones, skin, etc., the podiatrist specialises in feet and touches on other related problems, such as back problems, and deals with correct gait and correct posture.
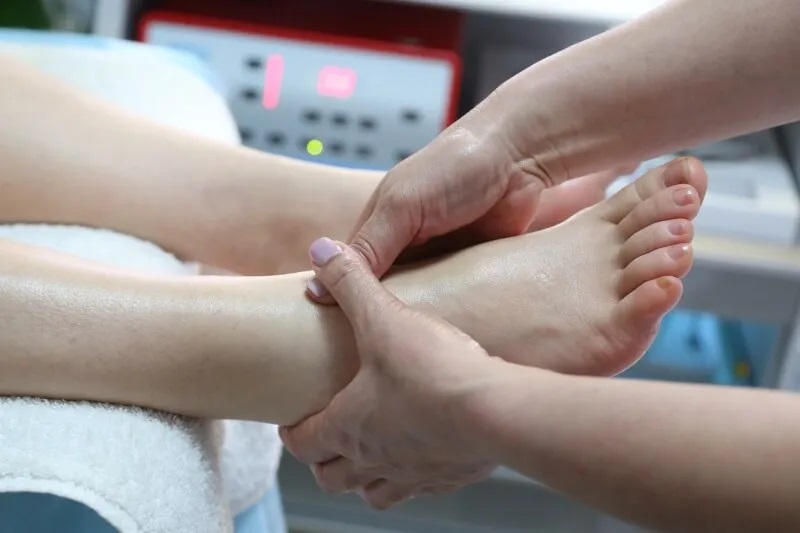
A podiatrist needs to know the basics of all associated medical disciplines - dermatology, orthopaedics, neurology, diabetology, rehabilitation, paediatrics, traumatology, algesiology, etc., as well as instrument pedicure, foot examination, production of individual orthopaedic aids and much more.
Podiatry thus brings together experts from many different subfields, under the auspices of the Czech Podiatric Society, which strives for the continuous education of its members. The Podiatric Outpatient Clinic focuses on the care of patients with diabetic foot syndrome, which is associated with vascular and nerve damage in diabetics.
Podologist
A podiatrist takes care of the feet, especially the nails; more often we meet the term pedicurist. Podologists are associated with the Czech Podological Society, which is dedicated to the further education of its members. The difference between a podiatrist and a podologist is described in more detail by MUDr. Marie Součková:
"Many people confuse the field of Podiatry (which is medical) with Podology. Podology is a non-medical field and includes treatment of problematic feet - by instrumental pedicure, treatment of nails (even ingrown) including their correction by the method of ortonyxia. This activity is performed by erudite pedicurists with medical education or specially trained pedicurists. They advise clients on appropriate skin care and nail care, as well as advice on footwear or the correct wearing of socks."
Orthopaedist
The orthopedist deals with the entire human musculoskeletal system, from developmental defects in children through injuries and degenerative joint diseases to oncological diseases. The orthopedist is responsible for prevention, treatment and rehabilitation. He has a medical degree in surgery with five years of experience in orthopaedics, so he is qualified to do his own practice on an outpatient basis.
Physiotherapist
A physiotherapist is an expert in human movement and rehabilitation, trying to restore the functionality of the body. He focuses on the prevention, diagnosis and therapy of musculoskeletal disorders, he looks at the person comprehensively and tries to reveal even remote causes of problems.
Also, the physiotherapist is university educated in a number of medical disciplines about the human body, such as anatomy, kinesiology, physiology, biomechanics, neurology and others. After graduation, he continues his education through professional courses and conferences to keep his knowledge and skills current.
The physiotherapist mainly examines by touch, uses functional tests to assess movement capabilities and performs movement analyses. Unlike a physical therapist, he or she is not authorized to perform or evaluate x-rays, CT scans, MRIs, SONOs, blood draws, or other methods themselves, but if a client brings in a similar examination from a physician, it helps refine the treatment process.
Associated experts
In order to provide our customers with objective information, we work closely with selected experts and draw the basis for our articles from verified sources. To round out the list, here is a list of other experts you may come across in the foot context:
- Algesiologist - treats chronic pain accompanying musculoskeletal disorders
- Biomechanist - deals with the mechanics of movement, analyses walking and running
- Dermatologist - skin doctor, specialising in the diagnosis and treatment of skin diseases and skin derivatives
- Diabetologist - specialist in patients with diabetes, ensuring proper metabolism and nutrition to prevent complications
- Aesthetic surgeon - orthopedic surgeon operating on foot deformities to improve the appearance and function of the foot
- Chiropractor - focuses on the diagnosis and manual treatment of mechanical joint disorders, especially of the spine
- Surgeon - operative treatment of diseases and injuries
- Massage therapist - provides body massage as part of rehabilitation and medical care
- Naturopath - folk healer who prefers natural and non-invasive treatment or self-medication of patients; this also includes homeopathy, Ayurveda, traditional Chinese and European medicine
- Osteopath - closely examines bones, joints, ligaments and other connective tissues; gently manipulates the client's body to eliminate problems
- Orthotist-prosthetist - in cooperation with a physician supervises the production and application of individual orthopaedic and prosthetic devices
- Rheumatologist - deals with diseases of the musculoskeletal system, especially stiff backs and joints
- Natural movement trainer - a lecturer specialising in the movement of the body in accordance with nature
